gridviz
Gridviz API reference
Table of contents
- Gridviz API reference
Anything unclear or missing? Feel free to ask !
Usage
Create a Gridviz map using const map = new gridviz.Map(); and customise it with the methods described in the documentation below.
Here’s a basic example that loads a CSV file on Europe population (5km resolution):
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
//set position and zoom
.setGeoCenter({ x: 4500000, y: 2900000 })
.setZoom(3000)
//add CSV layer
.addCSVGridLayer(
//data URL
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eurostat/gridviz/master/assets/csv/Europe/pop_2018_5km.csv',
//resolution, in CRS unit (m)
5000,
//the style
[
new gridviz.SquareColorWGLStyle({
//the CSV column to show
colorCol: 'Population',
//value to [0,1] mapping function, see [below](#stretching)
tFun: (value) => gridviz.sExp(Math.min(value / 100000, 1), -15),
}),
]
)
Gridviz can display several layers on top of each others. Each layer is based on a single multi-resolution dataset, which can be displayed with several cartographic styles. For more information, see the examples.
Map Configuration
The following methods allow further configuration of a Gridviz map:
| Method | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| map.getGeoCenter() map.setGeoCenter([value]) |
{ x:number, y:number } | { x:0, y:0 } | Get/set the geographical coordinates of the view center. |
| map.getZoom() map.setZoom([value]) |
number | 1 | Get/set the view zoom. This is expressed as the size of a pixel in ground distance. |
| map.getZoomExtent() map.setZoomExtent([value]) |
Array(number) | [0, Infinity] | Get/set the view zoom extent, in order to prevent the user to zoom in/out beyond some zoom levels. |
| map.getBackgroundColor() map.setBackgroundColor([value]) |
string | “white” | Get/set the map background color. |
| map.getBoundaryLayer() map.setBoundaryLayer([value]) |
LineLayer / object | undefined | A layer for boundary lines, see here. |
| map.getLabelLayer() map.setLabelLayer([value]) |
LabelLayer / object | undefined | A layer for labels (such as placenames), see here. |
| map.addBackgroundLayer([options]) | object | Add a background image layer, see here. | |
| map.addZoomButtons([options]) | All properties are optional { id: HTML element id, class: HTML element CSS class, x: CSS 'left' property, y: CSS 'top' property, onZoom: Custom event handler when user clicks zoom in or out, delta: The delta applied to each zoom event. } |
{ id: ‘gridviz-zoom-buttons’, x: map width - 50, y: 10, onZoom: undefined, delta: 0.2 } | Add zoom in and zoom out buttons to the viewer. |
| map.addFullscreenButton([options]) | All properties are optional { id: HTML element id, class: HTML element CSS class x: CSS 'left' property, y: CSS 'top' property } |
{ id: ‘gridviz-zoom-buttons’, x: map width - 50, y: 10 } | Add a button to the viewer that toggles fullscreen mode. |
| map.setViewFromURL() | Set view geo center and zoom from URL parameters x, y and z. For example, using the URL myPage.html?x=1000&y=2000&z=45 will force the viex to center to geographical coordinates (1000, 2000) and zoom 45. | ||
| map.redraw() | Force the map to redraw. | ||
| map.destroy() | Destroy the map, canvas, legend and tooltip and remove their event listeners. |
Map options object
When building a gridviz map, in addition to the container element you can also specify an options object with the properties outlined in the table below.
For example:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv, {
w: 600,
h: 600,
legendDivId: 'myLegendDiv',
selectionRectangleColor: 'red',
selectionRectangleWidthPix: () => '1',
backgroundColor: 'white',
tooltip: {
fontSize: '1.2em',
transitionDuration: 100,
},
onZoomStartFun: (event) => {
console.log('pan/zoom start', event)
},
onZoomFun: (event) => {
console.log('zoom', event)
},
onZoomEndFun: (event) => {
console.log('pan/zoom end', event)
},
})
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| opts.canvas | HTMLCanvasElement | created automatically by gridviz | Specify your own canvas element upon which gridviz will be rendered. |
| opts.w | number | container.offsetWidth | The width of the canvas. |
| opts.h | number | container.offsetHeight | The height of the canvas. |
| opts.legendDivId | string | ‘gvizLegend’ | The identifier of the element upon which the legend will be appended. |
| opts.selectionRectangleColor | string | ‘red’ | The colour of the outline when a cell is highlighted. |
| opts.selectionRectangleWidthPix | Function | (r,z) => 4 | A function specifying the thickness in pixels of the outline when a cell is highlighted. The function parameter r is the cell resolution. z is the zoom level. |
| opts.transparentbackground | boolean | false | Whether the background should be filled with colour (backgroundColor) or not. It is essentially the difference between using context.fillRect vs context.clearRect. |
| opts.backgroundColor | string | ‘white’ | The background color of the canvas when transparentBackground is set to false. |
| opts.disableZoom | Boolean | false | Disables d3 pan and zoom when set to true. |
| opts.onZoomStartFun | Function | null | Event handler for when a pan/zoom event is initiated. |
| opts.onZoomFun | Function | null | Event handler for when a pan/zoom event is occurring. |
| opts.onZoomEndFun | Function | null | Event handler for when a pan/zoom event has finished. |
| opts.tooltip | Object | undefined | See tooltip docs |
Multi layer, multi style and multi scale mapping
A Gridviz map is organised as a stack of layers accessible through myMap.layers property. Each layer shows data from one single dataset myLayer.dataset, following a list of styles myLayer.styles. The map can adapt to the visualisation scale/zoom level with the following mechanisms:
- Multi-resolution datasets can be defined, so that different grid resolutions can be shown depending to the zoom level, see the multi-scale datasets in the next section.
- The layers and styles can be restricted to some scale, using their minZoom and maxZoom properties to define the zoom ranges for which they will be shown.
- Most style parameters are not static values, but functions of various parameters, including the map , usually noted z (for “”) which represent the size of a pixel screen in ground meter. Style parameters can thus be defined depending on the zoom level so that they adapt to the visualisation scale.
- Transparency can be defined at layer or style level with their alpha and blendOperation properties (see CanvasRenderingContext2D globalAlpha and globalCompositeOperation properties). These values are also not static, but functions of the z. It is thus possible to define the transparency depending on the zoom level,so that a layer or a style fades away when zooming in or out.
For further information, see the examples.
Adding data
Input data are tabular data, in CSV format.
For the position of the cell, two columns x and y must be specified, with the geographical coordinates of the lower left corner of the cell, expressed in the grid Coordinate Reference System. If this information is not explicitelly provided in the input data, it is however possible to compute it on-the-fly as explained here.
It is possible to specify different data sources for different zoom levels, so that the level of detail of the data can adapt to the zoom level. Tiled data can also be specified following the tiled format.
Are are several examples:
Single CSV file
This is the simplest case, when a unique CSV file is loaded. See the basic example above.
Multi scale CSV data
When several CSV files contain the data with different resolutions, it is possible to define a multi-scale dataset from those files. The change of dataset depending on the zoom level is controled with the minPixelsPerCell parameter:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
//set position and zoom
.setGeoCenter({ x: 4500000, y: 2900000 })
.setZoom(3000)
//add multiscale CSV layer
.addMultiScaleCSVGridLayer(
//array of resolutions, in CRS unit (m)
[5000, 10000, 20000, 50000, 100000],
//function which returns the URL for each resolution value
(r) =>
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eurostat/gridviz/master/assets/csv/Europe/pop_2018_' +
Math.round(r / 1000) +
'km.csv',
//the styles
[
new gridviz.SquareColorWGLStyle({
colorCol: 'population',
tFun: (value, resolution, stats) => gridviz.sExp(value / stats.max, -50),
}),
],
{
//the maximum pixel size before jumping to a lower resolution
minPixelsPerCell: 3,
}
)
Tiled data
For large datasets, it is recommended that you decompose them into different data chunks and index them by geographical location, as specified in the tiled format specification. The Gridviz map can then automatically retrieve only the useful data that falls into the viewer’s geographical extent. Here is an example of how to load such data:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
//set position and zoom
.setGeoCenter({ x: 4500000, y: 2900000 })
.setZoom(3000)
//add multi scale tiled layer
.addTiledGridLayer(
//data URL
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jgaffuri/tiledgrids/main/data/europe/population2/5000m/',
//the styles
[
new gridviz.SquareColorWGLStyle({
colorCol: 'TOT_P_2021',
tFun: (value) => gridviz.sExp(Math.min(value / 100000, 1), -15),
}),
]
)
Multi scale tiled data
Multi scale tiled data based on the tiled format can also be simply loaded with the example below. Here again, the change of dataset depending on the zoom level is controled with the minPixelsPerCell parameter:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
//set position and zoom
.setGeoCenter({ x: 4500000, y: 2900000 })
.setZoom(3000)
//add multi scale tiled layer
.addMultiScaleTiledGridLayer(
//array of resolutions, in CRS unit (m)
[5000, 10000, 20000, 50000, 100000],
//function which returns the URL for each resolution value
(r) =>
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jgaffuri/tiledgrids/main/data/europe/population2/' + r + 'm/',
//the styles
[
new gridviz.SquareColorWGLStyle({
colorCol: 'TOT_P_2018',
tFun: (value, resolution, stats) => gridviz.sExp(value / stats.max, -50),
}),
],
{
//the maximum pixel size before jumping to a lower resolution
minPixelsPerCell: 3,
}
)
| Method | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
| map.addCSVGridLayer([args]) | See example | Add a layer from a CSV grid dataset. |
| map.addMultiScaleCSVGridLayer([args]) | See example | Add a layer from a multi scale CSV grid dataset. |
| map.addTiledGridLayer([args]) | See example | Add a layer from a tiled grid dataset. |
| map.addMultiScaleTiledGridLayer([args]) | See example | Add a layer from a multi scale tiled grid dataset. |
To manage creation of datasets and their possible reuse accross different layers (so that the data is loaded and stored once), the following methods are also available:
| Method | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
| map.addLayer([args]) | - | Add a layer to the map. |
| map.makeCSVGridDataset([args]) | - | Make a CSV grid dataset. |
| map.makeTiledGridDataset([args]) | - | Make a tiled grid dataset. |
| map.makeMultiScaleCSVGridDataset([args]) | - | Make a multi scale CSV grid dataset. |
| map.makeMultiScaleTiledGridDataset([args]) | - | Make a multi scale tiled grid dataset. |
Data pre-processing and filtering
Input data can be processed/transformed before it is being used by the Gridviz map in order to, for example:
- Filter/simplify the data to keep only the necessary one. This allows saving client memory,
- Extract/compute each cell coordinates into the x and y columns, in case the input data does not contain such columns explicitelly,
- Compute a new column from the combination of existing ones, such as the ratio between two columns, or the aggregation of several columns,
- Run some data conversions, simplifications, aggregations, etc.
- Etc.
This process is run on each cell individually, only once, after the data has been downloaded.
Here is an example showing how to compute a new column on population change, as the difference between two columns TOT_P_2021 and TOT_P_2011. This new column is then used directly to be shown on the map:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
.setGeoCenter({ x: 4500000, y: 2900000 })
.setZoom(3000)
.addMultiScaleTiledGridLayer(
[1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 20000, 50000, 100000],
(r) =>
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jgaffuri/tiledgrids/main/data/europe/population2/' + r + 'm/',
[
new gridviz.ShapeColorSizeStyle({
/* style construction ... */
}),
],
{
preprocess: (c) => {
//for each cell, compute 2011 -> 2021 change and store it in a new "change" column
if (!c.TOT_P_2011 && !c.TOT_P_2021) c.change = 0
else if (!c.TOT_P_2011 && c.TOT_P_2021) c.change = +c.TOT_P_2021
else if (c.TOT_P_2011 && !c.TOT_P_2021) c.change = -c.TOT_P_2011
else c.change = c.TOT_P_2021 - c.TOT_P_2011
//remove unused information
delete c.TOT_P_2006
delete c.TOT_P_2011
delete c.TOT_P_2018
delete c.TOT_P_2021
},
minPixelsPerCell: 3,
}
)
Note that it is unfortunatelly currently not possible to compute new columns from the combination of two different datasets.
The preprocess function can also be used to remove/filter unnecessary cells and release memory resources. This can be achieved by returning false for the cells to remove.
Here is an example showing how to keep only the cells with specific values 41:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
.setGeoCenter({ x: 4500000, y: 2900000 })
.setZoom(3000)
.addMultiScaleTiledGridLayer(
[500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 20000, 50000, 100000],
(r) => 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jgaffuri/tiledgrids/main/data/europe/clc/' + r + 'm/',
[
/* define the style) */
],
{
minPixelsPerCell: 3,
//select cells with clc=41
preprocess: (c) => +c.clc == 41,
}
)
Basic styles
Shape/Color/Size Style
This style is a generic style which allows to define the shape, color and size of each grid cell, independantly according to 3 different variables. Three shapes are currently available: square, circle and donut (a disk with a hole of changing size). To show grid cells as small squares with only changing color, one of the styles based on web GL here or here should rather be used, for efficiency reasons.
See this example with changing size (code).
See this example with changing size and color (code).
See this example with random shape, color and size (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| color | function(c,r,z,vs):string | () => “#EA6BAC” | A function computing the color of a cell c, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. |
| size | function(c,r,z,vs):number | (c,r) => r | A function computing the size of a cell c in geographical unit, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. |
| shape | function(c,r,z,vs):string | () => “square” | A function computing the shape of a cell c, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. Expected values are within {“square”, “circle”, “diamond”, “donut”, “none”} |
Square color WebGL Style
This style displays each cell as a square, with a changing color. This style uses webGL and should thus be used to display grid cells at detailled resolutions.
See this basic example (code).
See this example with dark style (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the color. |
| tFun | function(v,r,s):number | (v, r, s) => v / s.max | A function computing the cell color parameter t (whithin [0,1]) from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, and statistics s. This t value is then used to determine the cell color from the color sampling. |
| stretching | {fun:string, alpha:number} | undefined | Necessary information to apply a stretching [0,1] -> [0,1] to the t value. Property fun is the type of function, among {“pow”, “powInv”, “exp”, “log”} - see stretching section for more information on those functions. This stretching is performed on GPU side (fragment shader). |
| colors | Array(string) | Colors based on interpolateSpectral | The sample of the color ramp. |
| color | function(t):number | undefined | Instead of specifying colors, this property can be defined. It is a function which returns a color from a t value within [0,1]. |
| opacity | function(r,z):number | undefined | A function returning the opacity of the style from the resolution r and z, within [0,1]. NB: If this opacity is defined, the individual color opacity will be ignored. |
| size | function(r,z):number | (r,z) => r + 0.2 * z | A function returning the size of the cells from the resolution r and z, in geographical unit. All cells have the same size. |
Square color category WebGL style
This style displays each cell as a square, with a changing color based on a categorical variable. This style uses webGL and should thus be used to display grid cells at detailled resolutions.
See this basic example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used to retrieve each cell category. | |
| color | Object, string -> color | undefined | The dictionary (string -> color) which give the color of each category. | |
| size | function(r,z):number | (r,z) => r + 0.2 * z | A function returning the size of the cells from the resolution r and z, in geographical unit. All cells have the same size. |
Composition style
This style shows a composition at cell level in various different ways: Flags, pie charts, rings, segments, radar, age pyramid and halftone.
See this basic example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| color | Object, string -> color | undefined | The dictionary (string -> color) which give the color of each category. | |
| type | function(c,r,z,vs):CompositionType | () => “flag | A function returning the symbol type of a cell c, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. CompositionType are among “flag”, “piechart”, “ring”, “segment”, “radar”, “agepyramid”, “halftone” | |
| size | function(c,r,z,vs):number | ((c,r) => r) | A function computing the size of a cell c in geographical unit, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. | |
| stripesOrientation | function(c,r,z,vs):number | () => 0 | For style types with stripes (flag, segment), a function returning the symbol stripes orientation (0 for horizontal, other for vertical) for a cell c, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. | |
| offsetAngle | function(c,r,z,vs):number | () => 0 | For radar, halftone or pie chart style, a function returning the offset angle for a cell c, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. The angle is specified in degree. The rotation is anti-clockwise. | |
| agePyramidHeight | function(c,r,z,vs):number | (c,r,z) => r | The function specifying the height of the age pyramid for a cell c, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. | |
| pieChartInternalRadiusFactor | number | 0 | For pie chart, this is parameter for internal radius, so that the pie chart looks like a donut. 0 for normal pie charts, 0.5 to empty half of the radius. |
Segment style
This style displays each cell as a segment with a changeable color, length, width and orientation.
See this basic example (code).
See this example with random segment orientation, color, length and width (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| orientation | function(c):number | () => 0 | A function computing the orientation (in degrees) of the segment representing a cell c. |
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the color. |
| color | function(v,r,s):string | () => “#EA6BAC” | A function computing the cell color from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, and statistics s. |
| lengthCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the segment length. |
| length | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v,r,s,z) => r | A function computing the segment length from its lengthCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| widthCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the segment width. |
| width | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v,r,s,z) => r | A function computing the segment width from its widthCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
Stroke style
This style shows the stroke of each cell with different colors, widths, shapes and sizes. This style can be used in addition to others to show the cell strokes on top of those other styles.
See this basic example (code).
See this an example with random color, size, width and shape (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| strokeColorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the stroke color. |
| strokeColor | function(v,r,s):string | () => “#666” | A function computing the cell stroke color from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, and statistics s. |
| sizeCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the size. |
| size | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v,r,s,z) => r | A function computing the cell size from its sizeCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| strokeWidthCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the stroke width. |
| strokeWidth | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v,r,s,z) => z | A function computing the cell stroke width from its sizeCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| shape | function(c):string | () => “square” | A function computing the shape of cell c. Expected values are within {“square”, “circle”, “diamond”, “none”} |
Advanced styles
Tanaka style
This style shows the grid cells in a Tanaka style, that is with discrete colors and a shadow effect.
See this basic example (code).
See this other example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| col | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the color. |
| tFun | function(v,r,s):number | (v, r, s) => (v - s.min) / (s.max - s.min) | A function computing the t parameter (whithin [0,1]) from the value v of col column, the resolution r and statistics s. |
| colors | Array(string) | [“#a9bb9e”, “#c9dcaa”, “#fde89f”, “#f9a579”, “#eb444b”] | The colors. |
| color | function(t):string | () => “gray” | If colors is not specified, the color ramp function. |
| nb | number | undefined | If colors is not specified, the number of colors. |
| colDark | string | “#111” | Shadow color: South East side. This should be a dark color. |
| colBright | string | “#ddd” | Shadow color: North West side. This should be a bright color. |
| widthFactor | number | 0.08 | Size of the shadow, as a portion of the resolution. |
Dot density style
This style displays each cell as randomly located points, with changeable density and color.
See this basic example (code).
See this example with random colors (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nbCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the dot number. |
| nb | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v, r, s, z) => 0.3 _ r _ r / (z _ z) _ v / s.max | A function computing the number of dots for a cell, from its nbCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| color | function(c):string | () => “#FF5733” | A function returning the color of the dots of a cell. Note that it is the same color for all dots within a cell. |
| dotSize | function(r,z):number | (r,z) => 2 * z | A function computing the dot size from the resolution r and z. It is the same size for all dots. |
| sigma | function(r,z):number | (r, z) => r * 0.4 | A function computing the sigma parameter of the dispertion (gaussian) of the dots around the cell center, from from the resolution r and z. It is the same sigma for all dots. |
Pillars style
This style shows the grid cells as 3D pillars or, with changeable height, width and color.
See this basic example (code).
See this basic example with simple style (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| heightCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the pillar height. |
| height | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v,r,s,z) => r | A function computing the pillar height from its heightCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the color. |
| color | function(v,r,s):string | () => “#c08c59” | A function computing the cell color from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, and statistics s. |
| widthCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the pillar width. |
| width | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v,r,s,z) => 0.5*r | A function computing the pillar width from its widthCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| simple | boolean | false | Set to true for a simplified drawing (as segments only, not entire pillar). |
| viewHeightFactor | number | 1.5 | The view height. |
| viewSX | number | 0 | The view X position. |
| viewSY | number | -0.5 | The view Y position. |
| shadowDirection | number | -40.3 * Math.PI / 180.0 | The shadow direction, in radian. |
| shadowFactor | number | 0.3 | A factor specifying the shadow length. |
| shadowColor | string | “#00000033” | The shadow color. |
| outlineCol | string | “#FFFFFF” | The pillar outline color. |
| outlineWidthPix | number | 0.5 | The pillar outline width, in pixels. |
Text style
This style shows the grid cells as text labels. The text, its color and font size can be set according to some cell values.
See this basic example (code).
See this example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| textCol | string | undefined | The name of the column/attribute of the tabular data where to retrieve the variable for text. |
| text | function(v,r,s,z):string | (v, r, s, z) => “X” | A function returning the text of a cell from its textCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column/attribute of the tabular data where to retrieve the variable for color. |
| color | function(v,r,s,z):string | () => “#EA6BAC” | A function returning the color of the cell from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| fontSizeCol | string | undefined | The name of the column/attribute of the tabular data where to retrieve the variable for font size. |
| fontSize | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v, r, s, z) => r * 0.8 | A function returning the font size of a cell in geo unit from its fontSizeCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| fontFamily | string | “Arial” | The text font family. |
| fontWeight | string | “bold” | The text font weight. |
Time series style
This style shows the grid cells as a time series chart. It is particulary suitable to show data that has high temporal granularity and low geographical granurality (variation across time rather than space). The time series charts can be colored and sized according to other variables.
See this basic example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ts | Array(string) | undefined | The columns of the time series, ordered in chronological order. Note that the style currently requires full time series, without missing data. |
| noData | function(string):boolean | (v) => v === undefined or v == “” or v === null or isNaN(+v) | A function specifying when a value should be considered as “no data” and thus not ignored. The line will have a break at these values. |
| offsetX | function(c,r,z):string | ()=>0 | A fonction computing the offset along X axis, in geographical unit, from origin point (lower left cell corner). This value is computed from the cell c, resolution r and z. |
| width | function(c,r,z):string | ()=>r | A fonction computing the chart width, in geographical unit. This value is computed from the cell c, resolution r and z. |
| offsetY | function(c,r,z):string | ()=>0 | Same as offsetX but along Y axis. |
| height | function(c,r,z):string | ()=>r | Same as width, but for the chart height. |
| anchorModeY | function(c,r,z):string | (c, r, z) => “center” | The anchor mode along Y axis: first to anchor to the first value, last for the last, bottom to anchor the minimum value to the bottom, top to anchor the maximum value to the top, center to center the chart along Y axis. |
| lineWidthCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the line width. |
| lineWidth | string | (v, r, s, z) => 1.5 * z | A function computing the cell chart line width in geographical unit from its sizeCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the color. |
| color | string | (v, r, s, z) => ‘black’ | A function computing the cell chart color from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
Side styles
The side styles are special:They do not display the cells, but their sides. They can be used to show discontinuities between cell values with, for example, some shadow effect.
Side style
This style displays the sides of the cells as segments with different colors and widths, depending on the values of the 2 adjacent cells.
See this example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| valueCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used to retrieve the cell values. | |
| value | function(v1,v2,r,s,z):number | (v1, v2, r, s, z) => 1 | A function computing the value of a cell side. This value is computed from the two adjacent cell values v1 and v2. For horizontal sides, v1 is the value of the cell below and v2 the value of the cell above. For vertical sides, v1 is the value of the left cell and v2 the value of the right cell. | |
| color | function(side,r,s,z):string | () => “#EA6BAC” | A function returning the color of a cell side side from the resolution r, statistics s and z. A side is represented as an object _{x:number,y:number,or:”v” | “h”,value:number}_. |
| width | function(side,r,s,z):number | (side, r, s, z) => r * side.value / 5 | A function returning the width of a cell side side, in geo unit, from the resolution r, statistics s and z. A side is represented as an object _{x:number,y:number,or:”v” | “h”,value:number}_. |
| orientation | number | 0 | Orientation of the sides. Set to 90 to show sides as slope lines for example. | |
| fillColor | function(c):string | undefined | A function returning an optional fill color for a cell c. |
Side category style
This style displays the sides of the cells as segments with different colors depending on the categories of the 2 adjacent cells.
See this example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| col | string | undefined | The name of the column used to retrieve the cell category. | |
| color | Object, string -> color | undefined | The dictionary (string -> color) which give the color of each category. | |
| width | function(side,r,z):number | (side, r, s, z) => r * 0.2 | A function returning the width of a cell side side, in geo unit, from the resolution r and z. A side is represented as an object _{x:number,y:number,or:”v” | “h”,value:number}_. |
| fillColor | function(c):string | undefined | A function returning an optional fill color for a cell c. |
Contour style
This style is experimental / under development. It displays the sides of the cells depending on discontinuities between the 2 adjacent cells, like contour lines.
See this example (code).
Isometric fence style
This style shows the composition of a total quantity into categories as vertical cross-sections oriented toward North-South and East-West. It is an alternative to composition style. It may also be seen as a bi-directional joyplot style showing categories - note that when angle value is set to 90°, the style is equivalent to a joyplot. This style was inspired by the USGS geologic isometric fence diagrams (1953).
See this example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| color | object | The dictionary (string -> color) which give the color of each category. | |
| heightCol | string | The column where to get the height values. | |
| height | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v, r, s, z) => r * 0.4 | A function returning the height of a cell from its value v, the resolution r, some statistics s and the z. |
| angle | number | 50 | The isometric perspective angle, in degree, within [-180,180]. |
| cornerLineStrokeColor | function(cell,r,z,angle): string | (c, r, z, angle) => “#999” | A function returning the corner line stroke style. |
| cornerLineWidth | function(cell,r,z,angle): number | (c, r, z, angle) => (angle % 90 == 0 ? 0 : 0.8 * z) | A function returning the corner line width. |
| sVert | boolean | true | Show vertical cross-sections. |
| sHor | boolean | true | Show horizontal cross-sections. |
Esthetic styles
JoyPlot Style
This style shows cell rows in the form of a ‘joyplot’ - named after Joy Division’s “Unknown Pleasures” album cover. For joyplot style showing composition by categories, or for various orientations and perspective angles, see isometric fence style.
See this basic example (code).
See this an example of shaded joyplot (code).
See this an example with random colors (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| height | function(c,r,z,vs):number | (c,r) => r*Math.random() | A function computing the height of a cell c in geographical unit, depending on its resolution r, the zoom z and an optional view scale object vs. |
| lineColor | function(y,ys,r,z):string | (y, ys, r, z) => “#BBB” | A function computing the line color from its y coordinate, statistics ys, the resolution r and z. |
| lineWidth | function(y,ys,r,z):number | (y, ys, r, z) => z | A function computing the line width from its y coordinate, statistics ys, the resolution r and z. |
| fillColor | function(y,ys,r,z):string | (y, ys, r, z) => “#c08c5968” | A function computing the line fill color from its y coordinate, statistics ys, the resolution r and z. |
Mosaic style
This style shows the cell as pseudo-irregular square shapes giving a mosaic effect. The cells are colored depending on a variable.
See this basic example (code).
See this roman style example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the color. |
| color | function(v,r,s):string | () => “#EA6BAC” | A function computing the cell color from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, and statistics s. |
| mosaicFactor | number | 0.15 | The mosaic factor, within [0,0.5], to control the shape irregularities. Set to 0 for no mosaic effect. Set to 0.5 for strong mosaic effect. |
| shadowFactor | number | 0.2 | The mosaic shadow factor, within [0,0.5]. Set to 0 for no mosaic shadow. Set to 0.5 for strong mosaic shadow. |
| shadowColor | string | “#555” | The mosaic shadow color. |
Ninja star style
This style shows the cell as a star polygon whose compacity depends on a variable. The higher the value, the more compact the star: Maximum values correspond to a square, and minimum values correspond to a thin star. The shapes in between correspond to 4 branches stars looking like a ninja star.
See this basic example (code).
See this other example (code) with stars parallel to the x/y axes.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| colorCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the color. |
| color | function(v,r,s):string | (v,r,s,z) => “#EA6BAC” | A function computing the cell color from its colorCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. |
| sizeCol | string | undefined | The name of the column used for the size. |
| size | function(v,r,s,z):number | (v,r,s,z) => t | A function computing the cell size, within [0,1], from its sizeCol value v, the resolution r, statistics s and z. 1 corresponds to a square, 0 to an infinitly thin cross. |
| shape | function(c):string | (c) => “o” | A function computing the orientation of the ninja star of a cell c: “o” for 45deg oblique star, “p” for a star parallel to the x/y axes. |
Lego style
This style shows the grid cells as lego bricks with changeable colors and height based on a quantitative variable.
See this basic example (code).
See this other example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| colors | Array(string) | [ “#00852b”, //darker green “#afd246”, //light green “#fac80a”, //dark yellow “#d67923”, //mostard “#bb805a”, //brown “#cb4e29”, //redish “#b40000”, //red “#720012”, //dark red ] | The colors. |
Other properties: See Tanaka style.
Lego category style
This style shows the grid cells as lego bricks with changeable colors based on a categorical variable.
See this basic example (code).
See this other example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| color | Object, string -> color | undefined | The dictionary (string -> color) which gives the color of each category. |
| colDark | string | “#333” | Shadow color: South East side. This should be a dark color. |
| colBright | string | “#aaa” | Shadow color: North West side. This should be a bright color. |
Kernel smoothing
This style allows applying a gaussian kernel smoothing to the input grid. Other styles can then be used on the smoothed grid - this style is thus more a ‘filter’ than a proper style.
Note that this style is available within the gridviz-smoothing extension which need to be added as: <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/gridviz-smoothing"></script>.
See this elementary example (code).
See this example (code).
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | function(cel):number | A function returning the value to consider for each cell. This is the value to be smoothed. | |
| sigma | function(r, z):number | The smoothing parameter (gaussian standard deviation), in geographical unit, computed from the resolution r and the z. The larger, the more smoothed. Note that for too small values, the approximation degrades significantly. | |
| factor | number | 2 | The smoothed grid may have a finer resolution than the input grid. This factor defines the smoothed grid resolution. When set to 1, the smoothed grid is exactly the screen resolution. Set to 2 to degrade the resolution to a factor 2. The higher, the more pixelised and the faster to compute. |
| filterSm | function(v):boolean | A filter function to filter the smoothed cells based on their smoothed value v. Return true to keep the cell, false otherwise. | |
| sCol | string | “ksmval” | The name of the attribute where the smoothed value is stored in the output smoothed grid. |
| styles | Array(Style) | The styles to represent the smoothed grid. |
The kernel smoothing computation relies on the fast-kde library, which produces smoothing approximation very fast. Note that the approximation degrades significantly for weak smoothing (for low sigma values).
Custom styles
Any need or idea for a new style ? feel free to ask or contribute !
Gridviz style library can easily be extended with new styles. See for example this custom style defined to draw cells as an arrow with a color depending on a statistical value population:
//create custom style
const customStyle = new gridviz.Style({
//define draw function
drawFun: (cells, resolution, cg) => {
//draw each cell as an arrow
//with a fill color depending on the property "population"
for (let cell of cells) {
//do not draw cells with no data or no population
if (!cell.population) continue
//set fill color as a shade from cyan to red depending on "population" property
const t = Math.floor((255 * Math.round(Math.pow(cell.population / 1000000, 1 / 5) * 6)) / 6)
cg.ctx.fillStyle = 'rgb(' + t + ',' + (255 - t) + ',' + (255 - t) + ')'
//fill arrow
cg.ctx.beginPath()
//left point
cg.ctx.moveTo(cell.x, cell.y)
//bottom center point
cg.ctx.lineTo(cell.x + resolution / 2, cell.y + resolution / 3)
//right point
cg.ctx.lineTo(cell.x + resolution, cell.y)
//top center point
cg.ctx.lineTo(cell.x + resolution / 2, cell.y + (resolution * 4) / 3)
cg.ctx.fill()
}
},
})
For more examples and inspiration, have a look at the code of existing styles here.
Legends
Gridviz offers different types of legends that are suited to different cartographic styles, namely:
- ColorCategoryLegend
- ColorDiscreteLegend
- ColorLegend
- SegmentOrientationLegend
- SegmentWidthLegend
- SizeLegend
The legends are appended to the div element specified in the legendDivId property in the App options object. If this is not specified then gridviz will generate one automatically.
Each layer style can have an array of legends.
To add a legend, simply push it to the corresponding legends array of that style, for example:
map.layers[0].styles[0].legends.push(
new gridviz.SizeLegend({
title: 'Number of inhabitants',
exaggerationFactor: 0.8,
shape: 'circle',
fillColor: '#e54f37',
})
)
For styling legends see Legend Styling.
ColorCategoryLegend

new gridviz.ColorCategoryLegend({
title: 'Dominant leaf type',
colCat: [
['#c6df58', 'None'],
['#9fd045', 'Mainly broadleaved'],
['#38a43b', 'Mainly coniferous'],
],
shape: 'square',
})
ColorDiscreteLegend
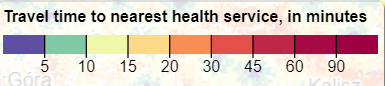
new gridviz.ColorDiscreteLegend({
title: 'Travel time to nearest health service, in minutes',
colors: ['#FDFECC', '#B2E3AA', '#6AC5A4', '#4FA1A2', '#427C9A', '#3E5791', '#3D3562', '#281A2C'],
breaksText: [5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90],
width: 300,
})
ColorLegend
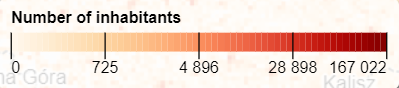
new gridviz.ColorLegend({
title: 'Number of inhabitants',
width: 400,
ticks: 5,
colorScale: d3.interpolateOrRd,
fun: (t, r, s) => s.max * gridviz.sExpRevInverse(t, -7),
})
SegmentOrientationLegend

new gridviz.SegmentOrientationLegend({
title: 'Population change',
labelUnitText: 'Strong increase',
color: '#d13c4b',
orientation: 60,
})
SegmentWidthLegend
new gridviz.SegmentWidthLegend({
title: 'Population in 2021',
labelUnitText: 'inhab.',
})
SizeLegend
new gridviz.SizeLegend({
title: 'Number of inhabitants',
exaggerationFactor: 0.8,
shape: 'circle',
fillColor: '#e54f37',
})
Legend styling
You can style each legend by using the ‘D3-like’ style() function after constructing your legend, like so:
new gridviz.SizeLegend({
title: 'Number of inhabitants',
exaggerationFactor: 0.8,
shape: 'circle',
fillColor: '#3E5791',
}).style('padding', '0px 5px')
Stretching
Most of Gridviz styles rely on a continuous mapping from a statistical variable to a visual variable (color, size, etc.). The statistical distribution can be stretched with one of the stretching functions listed below can be used. These functions have different properties and should be chosen according to the data distribution. The amplitude of the stretching can be adjusted with a parameter.
| Stretching function | Description | Stretching parameter |
|---|---|---|
| powerScale | Polynomial function | Power exponent, from 0 to Infinity. No change: 1 |
| logarithmicScale | Exponential function | Logarithmic base, from -Infinity to Infinity. No change: 0 |
| powerInverseScale | Polynomial inverse function | Power exponent, from 0 to Infinity. No change: 1 |
| exponentialScale | Exponential | Logarithmic base, from -Infinity to Infinity. No change: 0 |
| circularScale | Circular | 0: no stretching. 1: perfect circle section |
| circularInverseScale | Circular | 0: no stretching. 1: perfect circle section |
For more information on these functions and an overview of how they differ, see:
- this example (code).
- the code
- those graphs
Background layer
Tiled layer
To add a background layer to a Gridviz map, use the following addBackgroundLayer method:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
(...)
.addBackgroundLayer({
url: "https://gisco-services.ec.europa.eu/maps/tiles/NaturalEarth/EPSG3035/",
resolutions: [156543.03392804097, 78271.51696402048, 39135.75848201024, 19567.87924100512, 9783.93962050256, 4891.96981025128, 2445.98490512564],
origin: [0, 6000000],
filterColor: (z) => "#ffffff66",
})
See this example (code).
A background layer must be based on an external tiled web map specified with the properties listed in the table below.
The addBackgroundLayer method has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | undefined | The base URL of the tiled web map. |
| urlFun | function(x,y,z):string | (x, y, z) => this.url + z + “/” + x + “/” + y + “.png” | The function returning a specific image URL from its (x,y,z) coordinates in the tiling scheme. |
| resolutions | Array(number) | undefined | The list of resolutions by zoom z level, starting with the zoom level with larger resolution to lower resolutions. |
| z0 | number | 0 | If number of the first zoom level (larger resolution), usually 0. |
| nbPix | number | 256 | The size of each tile image, in pixel number, usually 256. |
| origin | Array(number) | [0, 0] | The geographical coordinates of top left corner of the tiling scheme. |
| visible | boolean | true | The visibility of the layer. When false, the layer is not drawn. |
| minZoom and maxZoom | number | 0 and Infinity | The min/maximum s to show the layer. Outside of this range, the layer is not drawn. |
| filterColor | function(z):string | undefined | A function returning a filter color from the z. This color alpha channel can be used to soften the background layer: Use “ffffffd1” for example. This color can addapt to the zoom level, so that the layer can progressively fade away when zooming out. |
For more information, see the code.
WMS
To add a WMS background layer to a Gridviz map, use the following addBackgroundLayerWMS method:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
(...)
.addBackgroundLayerWMS({
url: 'https://sgx.geodatenzentrum.de/wms_basemapde?&service=WMS&request=GetMap&layers=de_basemapde_web_raster_grau&styles=&format=image%2Fjpeg&transparent=false&version=1.1.1&srs=EPSG%3A3035',
maxZoom: 50,
})
See this example (code).
The addBackgroundLayer method has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | undefined | The base URL of the WMS. This URL must contain all necessary parameters, except width, height and bbox which are computed by the application. |
| visible | boolean | true | The visibility of the layer. When false, the layer is not drawn. |
| minZoom and maxZoom | number | 0 and Infinity | The min/maximum s to show the layer. Outside of this range, the layer is not drawn. |
| filterColor | function(z):string | undefined | A function returning a filter color from the z. This color alpha channel can be used to soften the background layer: Use “ffffffd1” for example. This color can addapt to the zoom level, so that the layer can progressively fade away when zooming out. |
For more information, see the code.
Foreground information
Showing labels
To show labels on top of a Gridviz map, use the following setLabelLayer method:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
(...)
.setLabelLayer({
url: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eurostat/euronym/main/pub/v3/UTF_LATIN/50/EUR.csv",
preprocess: lb => {
//project from geo coordinates to ETRS89-LAEA
const p = proj([lb.lon, lb.lat])
lb.x = p[0]; lb.y = p[1];
delete lb.lon; delete lb.lat;
},
style: (lb, z) => {
//select label based on
if (lb.rs < z) return;
//set style based on
if (lb.r1 < z) return "1em Arial";
return "1.5em Arial";
},
haloColor: () => "cyan"
})
Input data need to be as a CSV table. Each row should correspond to a label, with a x and y column for the label position, and a name column for the text to write. The data can be restructured on the fly after loading to meet this requirement using the preprocess function.
For European grids based on ETRS89-LAEA CRS, the gviz_es.getEuronymeLabelLayer() function from gridviz-eurostat module returns ready-to-use label layer settings based on Euronym which allow zoom dependant label selection.
The setLabelLayer method has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | undefined | The URL of the label CSV file. The file should contain the information for each label such as the text, the position and other information for the display of the label according to the zoom level. If necessary, this data can be reformated with the preprocess function. |
| style | function(lb,z):string | () => “bold 1em Arial” | A function returning the style of the label lb for z. |
| dark | boolean | undefined | Set to true if the map is dark, so that the label default colors are suitable. |
| color | function(lb,z):string | opts.dark ? () => “#ddd” : () => “#222” | A function returning the color of the label lb for z. |
| haloColor | function(lb,z):string | opts.dark ? () => “#000000BB” : () => “#FFFFFFBB” | A function returning the halo color of the label lb for z. |
| haloWidth | function(lb,z):string | () => 4 | A function returning the halo width of the label lb for z. |
| textAlign | CanvasTextAlign | “start” | The anchor where to write the label, from its (x,y) position. See HTML-canvas textAlign property. |
| offsetPix | Array(number) | [5, 5] | Offset displacement for each label position, in pixel. |
| preprocess | function(lb):boolean | undefined | A preprocess to run on each label after loading. It can be used to apply some specific treatment before, format the label data, project coordinates, etc. This method may also be used to filter unecessary label by returning false for the labels not to keep. |
For more information, see the code.
Showing boundaries
To show boundaries on top of a Gridviz map, use the following setBoundaryLayer method:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
(...)
.setBoundaryLayer({
url: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eurostat/Nuts2json/master/pub/v2/2021/3035/03M/nutsbn_3.json",
color: (f, z) => {
const p = f.properties
if (p.co === "T") return "#888"
if (z < 400) return "#888"
else if (z < 1000) return p.lvl >= 3 ? "" : "#888"
else if (z < 2000) return p.lvl >= 2 ? "" : "#888"
else return p.lvl >= 1 ? "" : "#888"
},
width: (f, z) => {
const p = f.properties
if (p.co === "T") return 0.5
if (z < 400) return p.lvl == 3 ? 2.2 : p.lvl == 2 ? 2.2 : p.lvl == 1 ? 2.2 : 4
else if (z < 1000) return p.lvl == 2 ? 1.8 : p.lvl == 1 ? 1.8 : 2.5
else if (z < 2000) return p.lvl == 1 ? 1.8 : 2.5
else return 1.2
},
lineDash: (f, z) => {
const p = f.properties
if (p.co === "T") return []
if (z < 400) return p.lvl == 3 ? [2 * z, 2 * z] : p.lvl == 2 ? [5 * z, 2 * z] : p.lvl == 1 ? [5 * z, 2 * z] : [10 * z, 3 * z]
else if (z < 1000) return p.lvl == 2 ? [5 * z, 2 * z] : p.lvl == 1 ? [5 * z, 2 * z] : [10 * z, 3 * z]
else if (z < 2000) return p.lvl == 1 ? [5 * z, 2 * z] : [10 * z, 3 * z]
else return [10 * z, 3 * z]
}
})
Input data are structured as a GeoJSON FeatureCollection of linear features.
The gviz_es.getEurostatBoundariesLayer() function from gridviz-eurostat module returns ready-to-use boundary layer settings based on Nuts2json datasets.
The setBoundaryLayer method has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | undefined | The URL of the boundaries GeoJSON file. The file should contain the information for each boundary line, the position and other information for the display of the boundary according to the zoom level. If necessary, this data can be reformated with the preprocess function. |
| preprocess | function(bn):void | undefined | A preprocess to run on each boundary after loading. It can be used to apply some specific treatment before, format the boundary data, project coordinates, etc. |
| color | function(bn,z):string | (f, z) => “gray” | A function returning the color of the boundary bn for z. |
| width | function(bn,z):string | (f, z) => 2 | A function returning the width of the boundary bn for z. |
| lineDash | function(bn,z):string | (f, z) => undefined | A function returning the dash model of the boundary bn for z. |
For more information, see the code.
Transparency
Tooltip

A ‘tooltip’ shows information related to the selected grid cell. The information shown for each selected cell can be specified at layer level using the cellInfoHTML parameter. See for example:
new gridviz.Map(containerDiv)
.setGeoCenter({ x: 4500000, y: 2900000 })
.setZoom(500)
.addCSVGridLayer(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/eurostat/gridviz/master/assets/csv/Europe/pop_2018_5km.csv',
5000,
[
new gridviz.SquareColorWGLStyle({
colorCol: 'population',
tFun: (value) => Math.min(value / 50000, 1),
}),
],
{
//tooltip content configuration
cellInfoHTML: (c) => 'The population of this cell is: <b>' + c.population + '</b> !',
}
)
By default, the cellInfoHTML function is a function returning a list of all cell properties. In case several layers are defined, the cellInfoHTML function of the top layer is used. If it is not defined, then the layer the cellInfoHTML function of the layer below is used instead. If no cellInfoHTML function is defined for all layers, then no tooltip is shown.
You can adjust the tooltip settings by specifying a tooltip object in the map options, using the following properties:
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| opts.div | String | ‘tooltip_eurostat’ | Specify the div id to use as a tooltip. If unspecified, one is created automatically. |
| opts.parentElement | HTMLelement | document.body | Specify the HTML element to which the tooltip will be appended |
| opts.transitionDuration | string | 100 | The duration in ms of the tooltip transition animation. |
| opts.xOffset | number | 30 | The X offset to apply to the position of the tooltip container. |
| opts.yOffset | number | 20 | The Y offset to apply to the position of the tooltip container. |
| opts.xMouseOffset | number | 0 | The X offset to apply to the position of the mouse when hovering a cell. |
| opts.yMouseOffset | number | 0 | The Y offset to apply to the position of the mouse when hovering a cell. |
| opts.maxWidth | string | 20em | The max width of the tooltip. |
| opts.fontSize | string | 1.2em | The tooltip font size. |
| opts.background | string | ‘white’ | The background color of the tooltip |
| opts.padding | string | ‘5px’ | The tooltip padding. |
| opts.border | string | ‘0px’ | The tooltip border CSS property. |
| opts.border-radius | string | ‘5px’ | The tooltip border-radius. |
| opts.box-shadow | string | ‘5px 5px 5px grey’ | The tooltip box-shadow. |
| opts.font-family | string | ‘Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif’ | The tooltip font-family. |
For more information, see the code.
Leaflet
Gridviz can be used with leaflet by using the leaflet-gridviz plugin
Usage:
// import leaflet-gridviz after importing leaflet
;<script src="https://www.unpkg.com/leaflet-gridviz"></script>
// create your leaflet map
let map = new L.Map('map', {
center: ['50.00754', '19.98211'],
})
// define your leaflet-gridviz layer
let gridvizLayer = new L.GridvizLayer(AppOptions)
// add it to the map
gridvizLayer.addTo(map)
//then customize it as you wish by using the gridviz map attached to our GridvizLayer...
gridvizLayer.map.addMultiScaleTiledGridLayer(etc)
Alright?
Anything unclear or missing? Feel free to ask !