GeoDiff
GeoDiff format specification
version: 0.9.1
GeoDiff format represents differences between two versions of a vector geospatial dataset. GeoDiff format can especially be used to store and share dataset updates.
It is assumed that:
- the dataset structure does not change between the two versions; only the content changes.
- the dataset features have an identifier, which is stable between the versions. This means that features which do not change or change only slightly between both versions should keep the same identifier.
Structure
-
A GeoDiff file describes only the features that have been inserted, deleted or modified. Unchanged features are not described.
-
A GeoDiff file has the same structure as the dataset it relates to (geometry type, attribute names and types, identifier), with an additional attributes named: GeoDiff.
Each instance represents:
- Either an inserted feature. For this case, the geometry and attribute values must be specified. The GeoDiff attribute must be set to I.
- Or a deleted feature. For this case, geometry and attribute values (other than the identifier) are not required. The GeoDiff attribute must be set to D.
- Or a Modified feature. For this case, modified elements (geometry and/or attribute values) must be specified. The other unchanged elements are not required. The GeoDiff attribute must be set to:
- G if the geometry only was modified,
- An if attribute values only were modified (n is the number of modified attributes. n is optional) and not the geometry,
- GAn if both the geometry and attribute values were modified.
Encodings
GeoDiff format does not require any specific encodings.
Any vector geospatial format can be used. Possible encodings are: GeoPackage, Shapefile, GeoJSON.
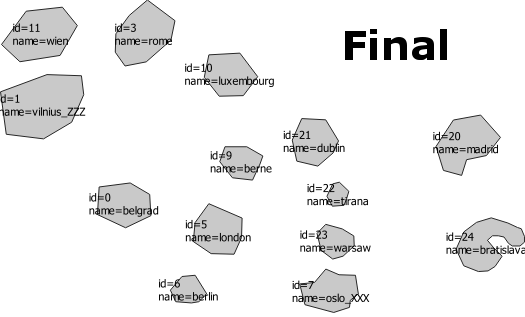
Example
 +
+ 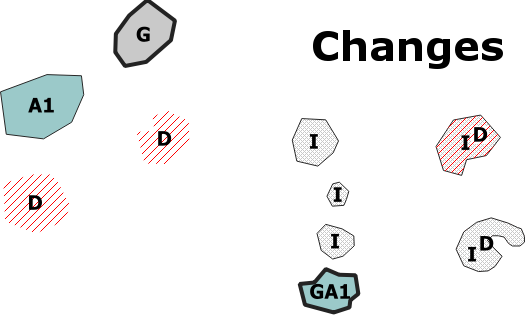 =
= 
Implementations
Contribution
For any suggestion, feel free to start a discussion or edit this page.